Top Help Desk KPIs to Improve Customer Support
May 6, 2025Unlocking Help Desk Success: The Power of KPIs
Want a better performing help desk? Tracking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for optimizing support operations and improving customer satisfaction. This listicle details seven essential help desk KPIs your team should be monitoring in 2025. Learn how to measure First Call Resolution rate, Average Response Time, Average Resolution Time, Ticket Volume and Distribution, Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), Cost per Ticket, and SLA Compliance Rate. Using these help desk KPIs will help identify areas for improvement, boost efficiency, and ensure your help desk drives customer loyalty and business growth.
1. First Call Resolution (FCR) Rate
First Call Resolution (FCR) rate is a crucial help desk KPI that measures the percentage of incoming support tickets resolved during the first interaction with the customer. This means the issue is completely addressed and the customer doesn't need to follow up with another call, email, or chat. FCR is a powerful indicator of both customer satisfaction and the efficiency of your help desk operations. A high FCR demonstrates that your team is effectively addressing customer needs on the first contact, leading to happier customers and reduced operational costs. This metric deserves its place on this list because it's a fundamental measure of a successful help desk strategy, directly impacting both the customer experience and your bottom line.

FCR is typically expressed as a percentage of total incoming requests and can be measured across various support channels like phone, email, and chat. It directly influences customer satisfaction metrics and provides clear insights into the effectiveness of your help desk team and the quality of your knowledge base. Features of a strong FCR strategy include clear resolution criteria, efficient workflow processes, and robust self-service resources. Benefits include improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and decreased workload for specialized teams.
Pros of Monitoring FCR:
- Reduces Operational Costs: Fewer follow-up interactions mean less time spent per ticket, optimizing agent productivity and minimizing overall support costs.
- Improves Customer Satisfaction: Resolving issues quickly and efficiently leads to happier customers and increased loyalty.
- Decreases Escalation Workload: A high FCR rate frees up escalation teams to handle more complex problems, improving overall team performance.
- Identifies Training Needs: Consistent tracking of FCR can highlight knowledge gaps within the team, allowing for targeted training and development initiatives.
Cons of Focusing Solely on FCR:
- Potential for Rushed Solutions: Agents may be incentivized to provide quick, but incomplete solutions to boost FCR numbers, negatively impacting customer satisfaction in the long run.
- Complexity of Issues: Some issues inherently require multiple interactions for complete resolution. Overemphasis on FCR can penalize agents dealing with these more complex cases.
- Standardization Challenges: Measuring FCR consistently across different communication channels can be difficult due to varying interaction styles and resolution processes.
- Conflict with Other KPIs: Focusing solely on FCR can sometimes conflict with other important help desk KPIs like Average Handle Time (AHT).
Examples of Successful FCR Implementation:
- Zendesk reports that companies achieving a 70% or higher FCR rate typically see a 30% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Apple's Genius Bar aims for an 80% or higher FCR rate for in-store technical support, emphasizing quick and efficient problem-solving.
- Cisco's technical support team achieved a 74% FCR by implementing improved knowledge base systems, empowering agents and customers with readily available information.
Tips for Improving FCR:
- Establish Clear Resolution Criteria: Define what constitutes a "resolved" issue to ensure consistent measurement and reporting.
- Implement Robust Knowledge Management Systems: Equip agents with easy access to comprehensive information and resources to resolve customer issues quickly.
- Provide Comprehensive Training and Support Tools: Invest in training and provide agents with the tools they need to efficiently diagnose and solve problems.
- Balance FCR Targets with Quality Metrics: Avoid focusing solely on FCR; balance it with other quality metrics to ensure thorough resolutions and avoid hasty fixes.
- Consider Weighted FCR Based on Issue Complexity: Implement a weighted FCR system that accounts for the varying complexity of different issues for a more accurate reflection of agent performance.
When and why should you use this approach? Implementing FCR tracking and improvement strategies is essential for any organization aiming to optimize its help desk operations and enhance customer satisfaction. By focusing on resolving customer issues during the first contact, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and build stronger customer relationships. For organizations handling high volumes of inquiries, particularly SaaS companies and digital service providers, FCR is a critical KPI for delivering a seamless and positive customer experience.
2. Average Response Time
Average Response Time (ART) is a crucial help desk KPI that measures the time elapsed between a customer submitting a support request (like a ticket, email, or chat message) and receiving the first response from a support agent. This KPI is essential for managing customer expectations and directly reflects the help desk's responsiveness and accessibility. It's a core component of evaluating help desk efficiency and a key indicator of customer satisfaction. Monitoring and optimizing ART is a foundational element for any organization striving to provide exceptional customer service.

ART is typically measured in minutes or hours and is often segmented by different factors to provide more granular insights. This segmentation can include communication channels (email, phone, chat, social media), ticket priority (critical, high, medium, low), and time of day (business hours vs. non-business hours). Different target ARTs are usually set for varying priority levels, reflecting the urgency of different issues. For example, a critical issue might have a target ART of 15 minutes, while a low-priority issue might have a target of 24 hours. This nuanced approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively and customer expectations are managed appropriately.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Salesforce Service Cloud: Customers using Salesforce Service Cloud who report average response times of under an hour often see a 30% increase in their Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores, demonstrating a clear link between responsiveness and customer happiness.
- HubSpot: HubSpot's service desk has achieved a 92% customer satisfaction rate by maintaining a first response time of fewer than 15 minutes during business hours. This highlights the importance of swift responses in a fast-paced business environment.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Support: AWS offers guaranteed response times based on the customer's support plan level, with critical issues on their Enterprise Support plan receiving responses in under 15 minutes. This tiered approach showcases how ART can be leveraged to differentiate service offerings.
Actionable Tips for Optimizing Average Response Time:
- Set Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establish specific SLAs for different issue priorities and their business impact. This formalizes response time expectations and provides a framework for performance measurement.
- Automate Acknowledgements: Implement automated acknowledgment systems to immediately inform customers that their request has been received. However, ensure these automated responses maintain a level of personalization to avoid feeling impersonal.
- Workforce Management: Utilize workforce management tools to forecast demand and ensure adequate staffing during peak periods. Proper staffing levels are essential for consistently meeting ART targets.
- Monitor Response Time Distribution: Don't just focus on the average. Analyze the distribution of response times to identify outliers and understand the factors contributing to longer delays.
- Customer-Specific Agreements: Consider establishing customer-specific response time agreements for key accounts, tailoring service levels to individual business needs.
Pros and Cons of Using Average Response Time as a KPI:
Pros:
- Strong correlation with customer perception of service quality
- Easy to measure and benchmark against industry standards
- Helps identify staffing needs and workload distribution issues
- Provides early warning signs of resource constraints
Cons:
- Fast responses don't guarantee quality resolutions
- Can incentivize premature or automated responses that add little value
- ART can fluctuate based on time of day and seasonal factors
- Different communication channels have varying customer expectations regarding response times
Why Average Response Time Deserves Its Place in the List of Help Desk KPIs:
ART is a fundamental help desk KPI because it directly impacts customer satisfaction and provides valuable insights into operational efficiency. Its ease of measurement and direct correlation with customer experience make it a powerful tool for improving service delivery. You can Learn more about Average Response Time and other best practices. For customer support teams, IT help desk professionals, and businesses handling high volumes of inquiries, tracking and optimizing ART is essential for maintaining a competitive edge and providing excellent customer service. Organizations seeking workflow automation and SaaS companies can leverage ART data to identify areas for improvement and enhance their service offerings. Even individuals and organizations using email for customer support can benefit from understanding and managing their average response times. The frameworks and standards promoted by the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), Service Desk Institute (SDI), and Help Desk Institute (HDI) underscore the importance of ART within the broader context of IT service management and help desk operations.
3. Average Resolution Time
Average Resolution Time (ART) is a crucial help desk KPI that measures the total time taken to resolve a customer issue, from the moment a ticket is opened to when it's finally closed. This metric provides a comprehensive view of your help desk's efficiency and directly correlates with customer satisfaction. A lower ART generally indicates a more responsive and effective support team, leading to happier customers and improved business outcomes. This makes ART a critical KPI for any organization aiming to optimize its help desk performance and enhance customer experience.
How it Works:
ART is calculated by summing the total time spent resolving all tickets within a given period and dividing it by the number of tickets resolved. This encompasses all time elapsed, including wait times, escalations, and hand-offs between different support agents or teams. It’s important to clarify whether the calculation uses business hours (e.g., 9 am - 5 pm, Monday to Friday) or calendar time (24/7), as this significantly impacts the final result.
Features and Benefits:
ART offers a granular view of help desk performance due to several key features:
- Measurement: Usually measured in hours or days, providing a readily understandable metric.
- Segmentation: Often segmented by issue type, priority, and complexity to pinpoint specific areas for improvement. This segmentation allows you to analyze trends within different support categories.
- Comprehensiveness: Includes all time elapsed, providing a complete picture of the resolution process.
- Flexibility: Can be calculated using business hours or calendar time to suit different reporting needs.
The key benefit of tracking ART is its direct impact on business continuity and productivity. By resolving issues quickly, you minimize downtime for users and ensure smooth business operations. Furthermore, ART helps identify bottlenecks in the resolution process, enabling data-driven decisions regarding staffing and resource allocation.
Pros and Cons:
While a powerful metric, ART has both advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Provides a complete view of the help desk's problem-solving efficiency.
- Directly impacts business continuity and productivity.
- Helps identify bottlenecks in the resolution process.
- Enables data-driven staffing and resource allocation decisions.
Cons:
- Can be skewed by extreme outliers (very complex cases). A single, exceptionally challenging issue can disproportionately inflate the average.
- May encourage premature ticket closure to improve metrics. Agents might be tempted to close tickets before fully resolving the issue, negatively impacting customer satisfaction.
- Doesn't account for differences in issue complexity without proper segmentation. Comparing ART across different support categories without considering complexity can be misleading.
- External dependencies may affect resolution time but be outside help desk control. Waiting for third-party vendors or other departments can increase ART, even if the help desk is performing efficiently.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several organizations have leveraged ART to improve their help desk performance:
- Microsoft: Reduced their internal IT help desk's ART from 2.4 days to 1.2 days by implementing AI-based ticket routing.
- IBM: Guarantees an ART of <4 hours for critical issues for premium support customers.
- Atlassian: Achieved a 40% reduction in ART by implementing improved knowledge management systems.
Tips for Improving Average Resolution Time:
- Categorization: Break down resolution time by issue category to identify specific problem areas. This allows for targeted interventions and process improvements.
- Tiered Support: Implement tiered support levels with clear escalation paths to ensure efficient handling of complex issues.
- Knowledge Management: Develop comprehensive knowledge base articles for common issues to empower both agents and customers with self-service solutions. Learn more about Average Resolution Time
- Feedback Loop: Monitor the relationship between resolution time and customer satisfaction to understand the impact of ART on customer experience.
- Automation: Use automation for routine tasks like ticket routing and notifications to free agent time for complex issues.
When and Why to Use ART:
ART should be a core metric for any organization operating a help desk or customer support team. It’s particularly relevant for businesses handling high volumes of inquiries, SaaS companies, digital service providers, and anyone using email for customer support. Tracking and analyzing ART provides invaluable insights into operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and areas for improvement within the support process. By actively monitoring and optimizing ART, businesses can streamline their help desk operations, enhance customer experience, and ultimately drive better business outcomes.
4. Ticket Volume and Distribution
Ticket Volume and Distribution is a crucial help desk KPI that tracks the total number of incoming support tickets and analyzes their distribution across various categories. This KPI provides a comprehensive view of your help desk's workload, allowing you to identify trends, allocate resources effectively, and proactively address emerging issues. Understanding and monitoring this KPI is essential for any organization striving to optimize its support operations and improve customer satisfaction. This deserves its place on the list of essential help desk KPIs because it provides a foundational understanding of your support workload, informing many other key performance indicators.
How It Works:
Ticket Volume and Distribution involves monitoring the influx of support requests over specific periods (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.) and categorizing them based on different parameters. These parameters can include:
- Issue Type: (e.g., hardware malfunction, software bug, billing inquiry, password reset)
- Source: (e.g., email, phone, chat, web form)
- Priority: (e.g., critical, high, medium, low)
- Time of Submission: (e.g., day of the week, time of day)
By analyzing these breakdowns, you can gain valuable insights into patterns and trends in support requests. For instance, a high volume of password reset requests might indicate a need for improved self-service password recovery options. Similarly, a surge in tickets related to a specific product feature after a recent update could highlight a usability issue.
Features and Benefits:
- Measures Total Tickets Received: Provides a clear picture of overall help desk workload.
- Categorization: Allows for granular analysis of ticket distribution by issue type, source, priority, and time.
- Pattern Identification: Reveals recurring issues, peak periods, and trends in support requests.
- Forecasting: Supports more accurate predictions of staffing needs and resource allocation.
- Context for Other KPIs: Provides valuable background information for interpreting other help desk KPIs, such as resolution time and customer satisfaction.
Pros:
- Proactive Capacity Planning: Enables data-driven resource allocation and staffing decisions.
- Identify Systemic Issues: Pinpoints recurring problems that may require broader solutions.
- Optimize Self-Service: Informs the development and improvement of self-service resources.
- Enhanced Understanding of Support Dynamics: Provides a comprehensive overview of help desk operations.
Cons:
- Volume Alone Isn't Everything: High ticket volume doesn't automatically indicate poor service; it could reflect growth or increased product complexity.
- Reliance on Accurate Tagging: Data accuracy depends on consistent and accurate ticket tagging by support agents.
- Seasonal Variations: Requires long-term analysis to account for seasonal fluctuations in ticket volume.
- Doesn't Measure Quality: Doesn't directly measure the quality of service provided.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- ServiceNow’s IT Service Management platform utilizes AI to forecast ticket volume with over 90% accuracy, enabling proactive resource planning.
- Zendesk benchmark data suggests that top-performing organizations maintain less than 20% variation between forecasted and actual ticket volumes.
- Dell Technologies reduced their support ticket volume by 25% by identifying and addressing recurring hardware issues uncovered through ticket distribution analysis.
Actionable Tips:
- Implement Consistent Tagging: Establish clear protocols for ticket categorization and tagging to ensure data integrity.
- Analyze Patterns for Staffing: Use volume patterns to optimize staffing schedules and ensure adequate coverage during peak periods.
- Prioritize Knowledge Base Development: Leverage ticket distribution data to identify topics that require more robust self-service resources. Learn more about Ticket Volume and Distribution
- Monitor Post-Release Volume: Track ticket volume trends after product releases or updates to quickly identify and address any emerging issues.
- Normalize Metrics: Compare ticket volume to user population growth to obtain normalized metrics that account for business expansion.
By effectively leveraging the Ticket Volume and Distribution KPI, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their help desk operations, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address emerging issues to enhance the overall customer experience. This makes it an indispensable tool for any business aiming to improve its support function.
5. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is a key help desk KPI that measures user satisfaction with the help desk service. It does this by directly surveying customers after a ticket is resolved. CSAT is typically presented as a percentage and provides crucial feedback on the quality of support delivered, directly from the customer’s perspective. This makes it a valuable counterbalance to purely operational metrics, which may not always reflect the customer experience. It reveals how well your help desk is meeting customer expectations and identifies areas for improvement.

CSAT is usually measured using a simple numerical scale, such as 1-5 or 1-10, with higher scores indicating greater satisfaction. These scores are then converted into a percentage. Data collection typically happens through post-resolution surveys, often triggered automatically after a ticket is closed. A key feature of CSAT is its ability to be segmented by various factors like issue type, agent, and resolution method. This allows for a granular understanding of performance across different areas of the help desk. Many CSAT surveys also include a space for qualitative feedback alongside the numerical rating, providing richer insights into the customer experience.
Using CSAT as one of your help desk KPIs is crucial for understanding the customer journey. It provides the direct voice-of-customer feedback necessary to gauge support quality. Furthermore, CSAT helps pinpoint high and low-performing agents or specific support areas that require attention. This data validates whether internal operational metrics are truly translating into tangible customer value. Ultimately, consistently monitoring and improving CSAT scores can predict customer retention and loyalty.
However, CSAT has some limitations. It can be susceptible to response bias, as highly satisfied or dissatisfied customers are statistically more likely to respond. External factors outside the help desk’s control, such as underlying product issues, can also influence scores. Over time, survey fatigue can reduce response rates, impacting data reliability. Finally, cultural differences may affect how rating scales are interpreted, requiring careful consideration when implementing CSAT globally.
Examples of successful CSAT implementation:
- Zappos: Maintains 95%+ CSAT scores by empowering agents to solve customer problems without strict time limits.
- American Express: Achieved 90% CSAT by implementing dedicated case ownership and personalized follow-ups.
- Intuit's TurboTax: Increased CSAT from 83% to 91% by implementing video-based support options during tax season.
Tips for effective CSAT implementation:
- Keep surveys brief and focused on the specific support interaction.
- Implement closed-loop processes to follow up on negative feedback.
- Correlate CSAT with other operational metrics to identify performance drivers.
- Share CSAT feedback directly with agents in near real-time for continuous improvement.
- Consider weighting CSAT scores based on issue complexity or business impact.
CSAT deserves a prominent place in any list of essential help desk KPIs because it directly reflects the customer’s perception of support quality. By understanding and acting on CSAT data, help desks can improve service delivery, increase customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive business growth. Learn more about Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT). This metric has been popularized by frameworks like the Net Promoter System, Gartner's Customer Experience Management framework, and the COPC Customer Experience Standard.
6. Cost per Ticket
Cost per Ticket is a crucial help desk KPI that measures the average financial expense associated with resolving a single support ticket. This metric provides valuable insights into the operational efficiency of your help desk from a financial perspective. By understanding the economic impact of your support operations, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, justify investments in improvement initiatives, and ultimately optimize your help desk performance. Its inclusion in the list of essential help desk KPIs stems from its ability to tie support performance directly to financial outcomes.
How it Works:
Cost per Ticket is calculated by dividing the total help desk costs by the number of tickets resolved. These costs encompass both direct expenses, such as staff salaries and technology investments, and often indirect costs, like facilities overhead and management expenses. For a more granular analysis, you can segment this KPI by ticket type, complexity, and resolution method. Tracking Cost per Ticket over time helps identify trends in efficiency and pinpoint areas for potential improvement. This allows you to understand, for example, if changes in staffing, software implementation, or process adjustments are positively impacting your bottom line.
Features:
- Formula: Total Help Desk Costs / Number of Tickets Resolved
- Cost Inclusion: Direct costs (staff, technology) and often indirect costs (facilities, management)
- Segmentation: Can be analyzed by ticket type, complexity, and resolution method
- Trend Analysis: Tracked over time to identify efficiency improvements or declines
Pros:
- Financial Accountability: Provides clear financial accountability for support operations, making it easier to track spending and identify areas for cost reduction.
- Investment Justification: Helps justify investments in automation, self-service tools, and other efficiency-boosting initiatives by demonstrating potential ROI.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Enables cost-benefit analysis of different support channels, allowing you to optimize resource allocation and channel strategies.
- Process Optimization: Identifies opportunities for process optimization by highlighting inefficiencies and areas where costs can be reduced.
Cons:
- Potential for Reduced Service Quality: Focusing solely on reducing cost per ticket can incentivize cost-cutting measures that negatively impact service quality and customer satisfaction.
- Calculation Complexity: Accurately calculating Cost per Ticket can be complex, especially when dealing with shared resources and indirect costs.
- Variability Based on Complexity: Without proper segmentation by ticket complexity, Cost per Ticket can be misleading, as complex issues naturally incur higher costs.
- Lack of Value Reflection: This KPI doesn't inherently reflect the value delivered to customers or the impact of support on customer retention.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- BMC Software: Reduced cost per ticket by 35% through the implementation of a chatbot for handling routine inquiries.
- IBM: Support cost analysis reveals that Level 1 support costs average $20 per ticket, while Level 3 engineering support averages $100+ per ticket, highlighting the importance of tiered support structures.
- Bank of America: Reduced help desk costs by $11 million annually by shifting 28% of tickets to self-service channels.
Tips for Using Cost per Ticket:
- Segmentation is Key: Segment your cost analysis by ticket complexity, resolution channel, and other relevant factors for a more accurate picture of your support spending.
- Balance with Quality: Balance cost metrics with customer satisfaction and service quality metrics to ensure cost reduction doesn't come at the expense of customer experience.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in the total cost of ownership (TCO) for software and hardware, including maintenance and support costs, when calculating your overall expenses.
- Analyze Channel Costs: Analyze the costs associated with different support channels (phone, email, chat, etc.) to identify the most cost-effective routing strategies.
- Track Prevention Metrics: Track Cost per Ticket alongside ticket prevention metrics to identify proactive measures that can reduce support volume and overall costs.
By carefully monitoring and analyzing Cost per Ticket, and using it in conjunction with other key help desk KPIs, you can gain valuable insights into the financial health of your support operations and make data-driven decisions to optimize efficiency and improve the overall customer experience.
7. SLA Compliance Rate
Among the most crucial help desk KPIs is SLA Compliance Rate. This metric measures the percentage of help desk tickets addressed and resolved within the predefined timeframes outlined in your Service Level Agreements (SLAs). Tracking SLA compliance is essential for managing customer expectations, ensuring consistent service delivery, and upholding contractual obligations with both internal and external customers. This KPI provides a quantifiable measure of how well your help desk adheres to its promised service levels, directly impacting customer satisfaction and your organization's reputation.
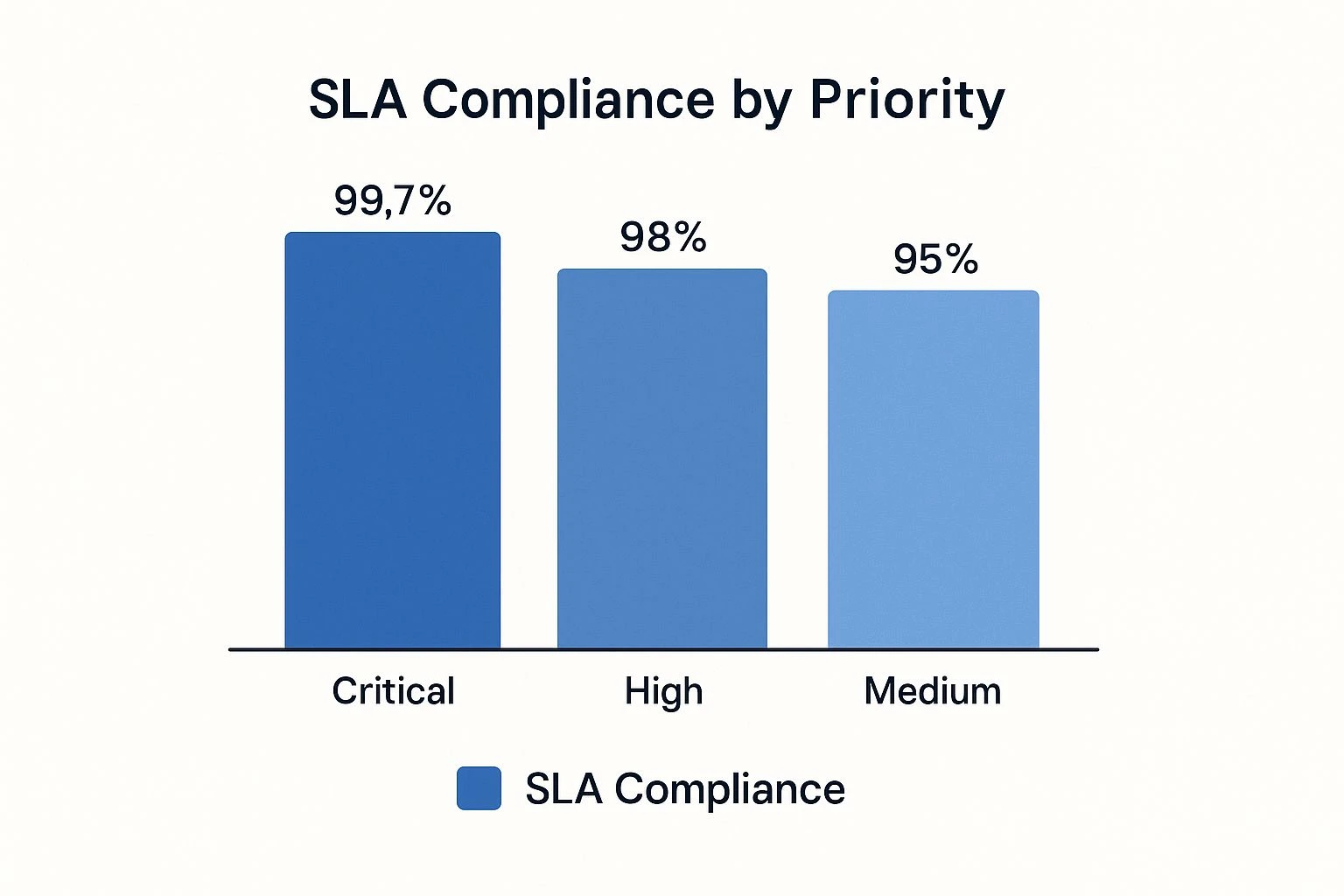
The infographic above visualizes data related to SLA compliance broken down by ticket priority. It highlights that while overall SLA achievement is at 92%, performance varies significantly across different priority levels. For instance, urgent "Priority 1" tickets boast a 98% compliance rate, reflecting a focused effort on addressing critical issues promptly. However, "Priority 3" tickets lag behind at 88%, indicating a potential area for improvement in managing less urgent but still important requests. This disparity underscores the importance of not just tracking overall compliance but also analyzing performance across different segments.
SLA Compliance Rate is typically expressed as a percentage and often differentiated by ticket priority levels (e.g., P1, P2, P3) and the specific services offered. It usually incorporates multiple time-based metrics, including initial response time and total resolution time, and can be measured at different stages of the ticket lifecycle. For example, a first response SLA might require acknowledging a ticket within 30 minutes, while a resolution SLA might mandate resolving the issue within 24 hours. This granular approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of help desk performance.
Features and Benefits of Tracking SLA Compliance Rate:
- Objective Measurement: Provides a clear, data-driven view of service delivery against established commitments.
- Systemic Issue Identification: Helps pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies affecting service performance.
- Proactive Management: Enables early identification and escalation of at-risk tickets to prevent SLA breaches.
- Clear Expectations: Sets transparent expectations for both customers and support teams regarding service delivery.
Pros:
- Provides objective measurement of service delivery against commitments
- Helps identify systemic issues affecting service performance
- Enables proactive management of at-risk tickets
- Creates clear expectations for both customers and support teams
Cons:
- Can lead to 'gaming the system' behaviors to meet targets if not managed carefully.
- May not accurately reflect actual customer satisfaction if SLAs are poorly designed or unrealistic.
- Complex tickets may legitimately require SLA exceptions, which need to be tracked and managed.
- Requires sophisticated tracking systems for accurate measurement and analysis.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Accenture reportedly maintains a 99.7% SLA compliance rate through predictive analytics that identify potential breaches before they occur.
- Salesforce guarantees 99.9% SLA compliance for priority cases, incorporating financial penalties for breaches.
- HP Enterprise Services improved their SLA compliance from 92% to 98% by implementing automated escalation workflows.
Actionable Tips for Improving SLA Compliance Rate:
- Tiered SLAs: Design tiered SLAs based on business impact and customer needs.
- Real-time Tracking: Implement real-time SLA tracking dashboards visible to all agents.
- Escalation Paths: Establish clear escalation paths for at-risk tickets.
- Regular Review: Regularly review and adjust SLAs based on evolving business requirements and customer feedback.
- Comprehensive SLAs: Include both operational (internal) and customer-facing SLAs.
When and Why to Use This KPI:
SLA Compliance Rate is a fundamental help desk KPI, relevant for any organization providing service-based support. It's especially critical for businesses handling high volumes of inquiries, those operating under contractual service agreements, and companies prioritizing customer satisfaction. This KPI helps ensure accountability, drive continuous improvement, and maintain a high level of service quality. Tracking and analyzing SLA compliance is crucial for identifying areas needing improvement and demonstrating the value of the help desk to the wider organization. This KPI is popularized by frameworks like ITIL, ISO/IEC 20000, and the Technology Business Management (TBM) framework. This makes it a widely recognized and respected metric within the IT service management industry.
Help Desk KPI Performance Comparison
| KPI Title | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Call Resolution (FCR) Rate | Medium: Requires clear resolution criteria, multi-channel tracking | Moderate: Training, knowledge base, support tools | High: Improves customer satisfaction, reduces costs | Helps desks aiming to minimize follow-ups and escalations | Directly correlates with customer satisfaction and efficiency |
| Average Response Time | Low to Medium: Needs SLA definitions, channel segmentation | Moderate: Workforce management, automation tools | Moderate to High: Faster initial response improves perceived service | Ideal for environments emphasizing quick engagement | Easy to measure; correlates with service perception |
| Average Resolution Time | Medium to High: Needs detailed tracking across issue types | Moderate to High: Tiered support, knowledge base, automation | High: Reflects full problem-solving efficiency | Used where total resolution speed impacts business continuity | Identifies bottlenecks; supports resource optimization |
| Ticket Volume and Distribution | Low to Medium: Requires accurate ticket categorization | Moderate: Tagging systems, analytics tools | Moderate: Provides workload, trend insights | Capacity planning and identifying recurring issues | Enables proactive staffing and ticket trend analysis |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | Low: Requires survey implementation and data collection | Low to Moderate: Survey tools and analysis | High: Direct customer feedback on support quality | Measuring customer perception post-support interaction | Validates service quality and predicts customer loyalty |
| Cost per Ticket | Medium to High: Needs accurate cost allocation and segmentation | High: Financial tracking systems and analysis | Moderate: Financial efficiency insights for budgeting | Managing operational expenses and ROI on support | Quantifies financial impact; helps justify investments |
| SLA Compliance Rate | Medium to High: Requires SLA design and real-time tracking | Moderate to High: Monitoring dashboards, escalation workflows | High: Ensures contractual fulfillment and service consistency | Critical for contracts and managing service commitments | Provides objective SLA adherence measurement |
Elevating Your Help Desk Performance
Effectively managing a help desk requires a data-driven approach. By focusing on key help desk KPIs like First Call Resolution (FCR) rate, Average Response Time, Average Resolution Time, Ticket Volume and Distribution, Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) score, Cost per Ticket, and SLA Compliance Rate, you can gain valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of your support operations. These metrics provide a clear picture of where your team excels and where improvements can be made. Mastering these help desk KPIs allows you to not only identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows but also enhance customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs.
The insights gleaned from tracking these KPIs are essential for making informed decisions about resource allocation, training initiatives, and process improvements. For example, a high average resolution time could indicate the need for better knowledge base resources or additional training for your support staff. Monitoring ticket volume and distribution can reveal trends and help you anticipate peak periods, enabling you to proactively adjust staffing levels. Ultimately, these metrics empower you to deliver a superior customer experience.
If your help desk operations include phone support, understanding relevant metrics in that area is equally crucial. For a deeper dive into specific call center metrics and how to use them effectively, check out this comprehensive list of call center performance metrics examples.
Taking actionable steps based on your help desk KPI data is the key to driving real change. Start by prioritizing the KPIs most relevant to your business goals. Implement a system for regularly tracking and analyzing these metrics, and establish clear targets for improvement. Remember that optimizing your help desk isn't a one-time fix; it's an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation. By consistently monitoring these help desk KPIs and making data-driven decisions, you can create a support team that’s not just reactive, but proactive and truly focused on delivering outstanding customer experiences. Empower your team with the knowledge and tools they need to thrive, and watch your customer satisfaction soar.